ConnectedGRC
Drive a Connected GRC Program for Improved Agility, Performance, and Resilience
-
BusinessGRC
Power Business Performance and Resilience
Discover ConnectedGRC Solutions for Enterprise and Operational Resilience
Explore What Makes MetricStream the Right Choice for Our Customers
Discover How Our Collaborative Partnerships Drive Innovation and Success
- Want to become a Partner?
Find Everything You Need to Build Your GRC Journey and Thrive on Risk
Learn about our mission, vision, and core values
Adopting an Integrated Approach to GRC - Sterling Bank
Building a holistic and integrated GRC program
The Client: Sterling Bank
Overview
As a result of a concentration in construction lending in 2007-2008, Sterling Bank faced a near-death experience. Thanks to timely outside investment and subsequent recapitalization, as well as the implementation of an integrated GRC program, the bank has since successfully recovered. Today, Sterling Bank is a trusted and leading community bank with over 9 billion USD in assets.
Sterling had discussed their need for a forward-looking approach to ERM and an integrated GRC program for quite some time. Following its near-collapse, included in their agreement with the Federal Reserve Bank was a clause on adopting a comprehensive risk management program, which included various other GRC components. The bank formulated a sound strategy for a results-oriented GRC program, leveraging its existing open and honest internal corporate culture, where communicating bad news was encouraged, and where teams came together to find solutions for pressing issues.

Solution
Towards a New Enterprise Risk Management Strategy
Sterling Bank's integrated GRC program served as a catalyst for the creation of a forward-looking and pervasive approach to risk management. The salient features of their risk strategy included:
A Strong Risk Governance Framework
At the crux of Sterling Bank's innovative approach to GRC was the creation of a dynamic risk framework. The bank consolidated the bulk of its risk information in a centralized and comprehensive manner. It then built a new risk governance structure to promote a holistic view of risk. They also effectively implemented a top-down and bottom-up approach to identifying, measuring, mitigating, and managing risks.
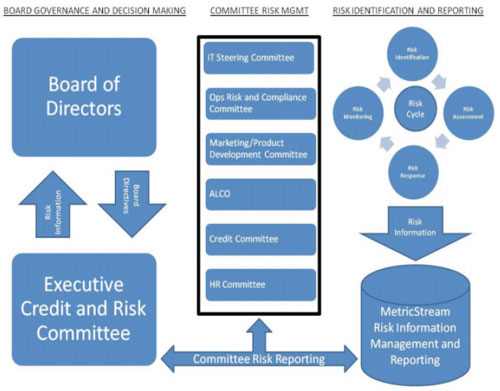
Referring to Figure 1; In the middle of the governance model are the various risk committees with senior level managers, who are assigned to specific risks. On the right is an illustration of the risk cycle comprised of various processes such as risk identification, risk monitoring, risk assessment and risk response. These generate the required risk information that is then channeled to various committees and the Executive Committee at the apex.
Best Practice
Sterling Bank maps its risks to its executive and other risk committees, in addition to tying the risks to its business objectives and strategies. These committees are responsible for ensuring that the strategic objectives are met, and that the risks are managed effectively. The bank has a mechanism in place for providing real time data to the committees, which helps steer the organization in the right direction.
A Clear Risk and Control Taxonomy
Sterling has created a rich and comprehensive risk and control taxonomy, which enables the board and senior management to get a thorough understanding of the risks faced by the bank. The executive risk committee must continuously and succinctly communicate the risk information to the board and senior management. A wellplanned and executed risk taxonomy based on a relatively simple model aids this process. The bank has identified and defined a few primary risk categories, and all of the risks identified across the bank can be easily rolled up into one of these categories. The executive risk committee then evaluates and assigns specific risk categories to the various committees. Following discussions, a final picture of risk is presented before the Board for its review and approval.
To facilitate Board reporting, the bank employs dashboards that clearly showcase the risk categories, as well as risk responses using color codes that indicate the level of risk. For example, different illustrations would highlight whether the risk is decreasing or remaining static. KRIs that are tied to each risk category are also represented.
A Common GRC Library
A core component of Sterling's GRC solution is the common GRC library. The bank's vision for a GRC library was very broad and all-encompassing. From the onset, the bank strived to achieve an integrated and pervasive GRC system, and wanted to avoid a piecemeal approach at all costs. Therefore, they developed an extensive GRC library consisting of ten different objects that are consistently tracked, including risks, controls, and processes; products, regulations and policies; and assets and asset classes. By tying all of these objects together, Sterling has the knowledge to drive a successful GRC program. Significant effort went into defining the GRC library, and arriving at a determined relationship between the individual objects. While the process of building and defining this GRC library was complex, the end result is a powerful resource for establishing a strong risk intelligent enterprise.
Efficient Compliance Testing and Self-Assessment
Sterling Bank had in place a very mature and robust compliance testing and self-assessment process. Following the adoption of their GRC strategy, they fully automated these processes for optimal results. Every month, the bank selects a sample of transactions and tests them for a series of specific compliance attributes, covering a range of regulations. Testers and risk professionals, such as credit analysts in lending units, are embedded within business units. This enables the bank to alleviate assurance fatigue. Sterling looks forward to expanding this practice across the enterprise.
Challenges Faced in GRC Program Implementation
Gaining Management Buy-In
One of the key challenges Sterling Bank faced during their GRC program implementation was gaining stakeholder buy-in. Not every stakeholder in the organization had the same level of commitment to their newly developed risk policy and the project at large. The business unit management, in particular, was focused more on revenue and production, and less on risk management. Therefore, the bank had to devise ways to eliminate "assurance fatigue” among risk managers, so that the GRC implementation was not viewed as a frustrating and complicated exercise.
Overcoming Lack of Formalized Guidelines on ERM
ERM as a discipline remains in a nascent stage and lacks an industry standardization or prescriptive format. For Sterling Bank, this meant they had the resources to build a GRC program, with no authoritative document to guide its strategies and decisions. Though it was a challenge, there was also an advantage; Sterling did not face any restrictions in adopting innovative new ways to achieve effective risk management.
Implementing an Effective Training Program
Educating employees on both the new risk management procedures as well as how to use the GRC tool was a demanding and resource intensive exercise. The task had to be handled along the same lines as that of change management. Employees across the newly structured bank also needed to be educated as to the rationale for a new risk program that included the articulation of the bank's vision that would guide them in their routine day-to-day processes and decision-making.
Adopting Robust Reporting
Implementing an efficient reporting mechanism was critical to adapting to the changing business requirements and conditions. Sterling Bank had a good risk architecture, risk library, and risk policies in place. However, different business units and teams provided several different risk reports, which had to be consolidated in order to gain one single common perspective across the enterprise. This was challenging, considering that the reports generated quickly lost their relevance and timeliness after a few days.
Technology as an Enabler
Sterling Bank leveraged MetricStream's GRC suite of solutions to enable the execution of their new risk management strategy, and also to strengthen the foundation of their newly established business structure and enterprise. Technology has powered the entire Sterling GRC program implementation, and has helped the bank overcome many challenges by doing the following:
- Served as a catalyst for establishing a sustainable risk culture across the organization
- Enabled the bank to track and trend data for management committee and Board reporting
- Provided capabilities to isolate changes in testing for immediate action
- Helped conduct a thorough risk evaluation, and gathered extensive risk information from across the enterprise
- Simplified the best practice of mapping risks to each risk committee, and corresponding business objectives
- Supported the bank in accurately defining its KRIs, which are used to guide and drive Board meetings on risk
- Enabled an aggressive and thorough approach to building a comprehensive GRC library which served as the foundation of the whole program
- Enabled the automation of Sterling's mature and robust Compliance Testing and Self-assessment processes
Lessons Learned
• It is imperative to gain management buyin so that risk management strategies and policies can be effectively and consistently implemented across the enterprise.
• The project scope must be well defined from the beginning. Sterling Bank realized that its plan to implement 13 modules of the software solution in one year was not practical, and was an aggressive approach prone to delays and lack of resources.
• The resource requirements must be accurately determined prior to the start of a GRC program implementation. Underestimating project resources can derail an organization's entire risk management program.
• Technology is an enabling tool that also requires reliable data to achieve the desired end results. Sterling Bank began with little content, but quickly utilized their GRC program as an exercise to define all of their risks and controls, and build a thorough content base.
Best Practices in GRC Program Implementation
• Create a well-defined GRC program, tailored to the internal needs and challenges of a company
• Thoroughly document all requirements, factoring in the scale and size of the project
• Avoid designing complex solutions that address every conceivable business scenario
• Deploy a phased approach during complex stages in the program
• Give sufficient time and resources to stakeholders to encourage active participation in the program implementation
Challenges
As a newly recapitalized bank, Sterling had huge volumes of risk information that existed in separate silos, and in a variety of formats including sharepoint, spreadsheets, and word documents. The bank needed a way to consolidate all of this risk information to provide the Board of Directors, senior management and line management with a single and unified view of risk. The bank's Board of Directors is comprised of seasoned business leaders with extensive banking experience, who expected actionable risk information and frequent opportunities for meaningful dialogues with the risk team. For the Board of Directors, it was critical that they had a clear idea of the specific areas that had elevated risks, and the corresponding response strategies and plans developed by the risk team.
In addition, Sterling Bank needed to integrate the fragmented risk management structures of their parent company and the bank itself, and also standardize all of the disparate processes. The answer to these complex challenges was a comprehensive and integrated GRC program that would drive a strong risk culture across the entire bank.
Benefits
- Sterling Bank's new GRC program gained regulatory approval, and has met the expectations and standards set by various regulatory bodies.
- The bank's executive risk team has been highly successful in gaining the buy-in from the management team and the Board of Directors - a crucial step in moving forward with new GRC processes and programs.
- The bank has established a system where every employee has a personal goal tied to risk management. Risk management is one of the four top corporate goals for the company, and is also tied to the company's appraisal system.
- The bank also ties accountability for risks to the various risk committee chairs, so that the tone for a sound risk culture is set from the top.
- Sterling Bank has built a single source of truth across the enterprise using a single risk framework and nomenclature.